A gum graft procedure, a common dental surgery aimed at addressing gum recession, typically takes between 45 minutes to 1.5 hours, depending on the extent of the recession and the technique used. The procedure involves taking tissue from the roof of the mouth or using donor tissue to cover exposed tooth roots, promoting gum health and preventing further damage. Factors such as the number of teeth requiring treatment and the patient's overall oral health can influence the duration. While the surgery itself is relatively quick, patients should plan for a full morning or afternoon appointment to account for pre-operative preparations and post-operative instructions from the dentist or periodontist. Recovery time varies, but most individuals can resume normal activities within a few days, with full healing taking several weeks.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Average Procedure Time | 1 to 2 hours per session |
| Type of Graft | - Connective Tissue Graft: 1.5 to 2 hours - Free Gingival Graft: 1 to 1.5 hours - Pedicle Graft: 1 to 2 hours - Allograft: 1 hour or less |
| Number of Teeth Treated | - Single tooth: 30 minutes to 1 hour - Multiple teeth: 1.5 to 2+ hours |
| Anesthesia Time | 10 to 15 minutes for local anesthesia administration |
| Preparation Time | 10 to 20 minutes (cleaning, marking, and positioning) |
| Suture Placement Time | 15 to 30 minutes |
| Recovery Time in Office | 10 to 15 minutes post-procedure monitoring |
| Total Appointment Duration | 2 to 3 hours (including pre- and post-procedure steps) |
| Factors Affecting Duration | - Graft complexity - Patient anatomy - Surgeon experience - Additional procedures (e.g., bone grafting) |
| Post-Procedure Instructions Time | 5 to 10 minutes for care instructions |
What You'll Learn

Pre-procedure preparation steps
Effective preparation for a gum graft procedure begins with a thorough consultation with your periodontist. During this visit, the specialist will assess your oral health, discuss the grafting technique (e.g., connective tissue, free gingival, or pedicle graft), and outline the expected duration of the procedure, which typically ranges from 30 minutes to 1.5 hours depending on complexity. This step is critical for setting realistic expectations and ensuring the procedure aligns with your specific needs.
Medication management is a key pre-procedure consideration. If you’re taking blood thinners (e.g., aspirin, warfarin, or clopidogrel), anti-inflammatory drugs, or supplements like fish oil, your periodontist may advise discontinuing them 7–10 days prior to surgery to minimize bleeding risks. Always follow their guidance, as abrupt cessation of prescribed medications can have serious health implications. For patients with conditions like diabetes or hypertension, stabilizing these through medication adherence is essential to prevent complications.
Dietary adjustments play a practical role in preparation. Avoid hard, crunchy, or sticky foods for at least 24 hours before the procedure, as these can irritate gums or dislodge existing tissue. Opt for soft, cool foods (e.g., yogurt, smoothies, or mashed vegetables) the day prior to reduce gum inflammation. Hydration is equally important—drink plenty of water, but avoid alcohol for 48 hours pre-procedure, as it can interfere with anesthesia and increase bleeding risks.
Practical at-home preparations can streamline your recovery. Stock up on post-procedure essentials like gauze, saltwater rinse ingredients (1 teaspoon salt per 8 ounces warm water), and soft-bristled toothbrushes. Arrange for transportation to and from the procedure, as local anesthesia may cause temporary numbness or disorientation. If the surgery is extensive, consider scheduling 2–3 days off work to allow for initial healing and rest.
Finally, mental preparedness can significantly impact your experience. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises or guided meditation in the days leading up to the procedure can reduce anxiety. Wear comfortable clothing to the appointment and bring headphones to listen to calming music during the surgery. Clear communication with your periodontist about any concerns ensures a collaborative approach, fostering confidence and a smoother process.
Numbing Gums for Deep Dental Cleaning: What to Expect at the Dentist
You may want to see also

Types of gum graft techniques
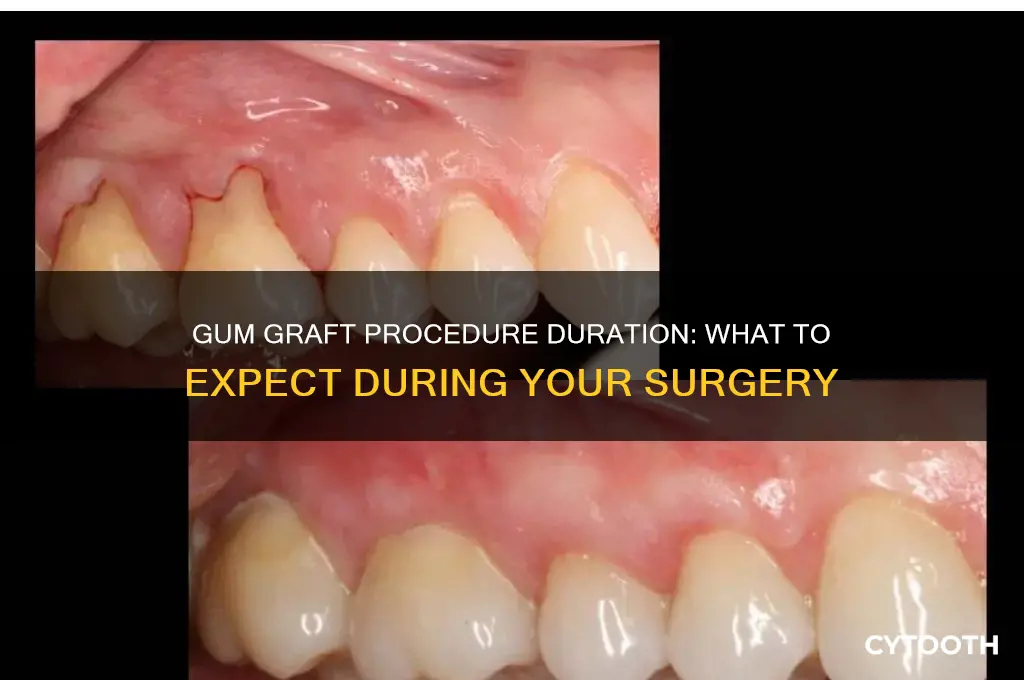
The duration of a gum graft procedure varies significantly based on the technique used, with each method tailored to address specific periodontal issues. Understanding these techniques not only clarifies the time investment but also highlights their unique benefits and limitations. Here’s a breakdown of the primary gum graft techniques and their typical procedural timelines.
Connective Tissue Grafts are the most common technique, often used to treat root exposure in younger adults (ages 20–50). The procedure involves harvesting tissue from the palate, creating a flap, and removing a small piece of connective tissue. This tissue is then sutured over the exposed root, typically taking 60–90 minutes per tooth. Post-operative care includes avoiding hard or crunchy foods for 1–2 weeks and using a chlorhexidine mouthwash (0.12% concentration) twice daily for 2 weeks to prevent infection.
Free Gingival Grafts are ideal for patients with thin gum tissue or those needing additional bulk. Unlike connective tissue grafts, this method removes a full layer of tissue from the palate, which is then directly stitched to the affected area. The procedure usually lasts 45–75 minutes per tooth but may cause more post-operative discomfort due to the palatal donor site. Patients are advised to apply ice packs for 20 minutes on, 20 minutes off, during the first 24 hours to minimize swelling.
Pedicle Grafts utilize adjacent gum tissue, eliminating the need for a second surgical site. This technique is suitable for patients with sufficient gum tissue near the affected area. The procedure involves rotating or repositioning nearby tissue to cover the exposed root, typically taking 45–60 minutes. While less invasive, it’s not applicable to all cases, particularly those with widespread recession. Post-procedure, patients should rinse with warm salt water (1/2 teaspoon per cup) for 1 week to aid healing.
Allograft Techniques employ donor tissue from a tissue bank, eliminating the need for a palatal harvest. This method is often chosen for patients with extensive recession or those unable to undergo a second surgical site. The procedure is quicker, usually completed in 30–45 minutes per tooth, but may require additional follow-ups to ensure proper integration. Patients are instructed to avoid brushing the graft site for 1 week and use a soft-bristled toothbrush thereafter.
Each technique offers distinct advantages, and the choice depends on the patient’s specific needs, tissue availability, and tolerance for recovery. Consulting a periodontist ensures the most appropriate method is selected, balancing procedural time with long-term outcomes.
Effective Ways to Heal Gum Cuts: Tips for Quick Recovery
You may want to see also

Average procedure duration
The typical gum graft procedure lasts between 30 minutes to 1.5 hours per quadrant of the mouth, depending on the technique used and the extent of gum recession. For patients requiring treatment in multiple areas, the total time can extend to 2–3 hours, though this is less common. Understanding these timeframes helps patients plan for the procedure and recovery, ensuring they allocate sufficient time away from daily activities.
Analyzing the factors influencing duration reveals that the type of graft plays a significant role. For instance, a connective tissue graft, which involves harvesting tissue from the palate, often takes longer than a pedicle graft, which uses adjacent gum tissue. Additionally, the number of teeth being treated and the complexity of the recession directly impact the overall time. Dentists typically assess these variables during the initial consultation to provide a more accurate estimate.
From a practical standpoint, patients should prepare for the procedure by arranging transportation, as local anesthesia is used, and its effects may linger post-surgery. Wearing comfortable clothing and bringing a soft, cool compress can aid in immediate post-procedure comfort. Avoiding strenuous activities for 48–72 hours is also recommended to prevent complications. These steps, combined with understanding the procedure’s duration, contribute to a smoother experience.
Comparatively, gum grafting is shorter than other dental surgeries like dental implants or full-mouth reconstructions, which can span multiple sessions. However, its focused nature requires precision, making the time investment crucial for long-term success. Patients often find that the relatively brief procedure time, coupled with proper aftercare, results in significant improvements in gum health and aesthetics.
In conclusion, while the average gum graft procedure takes 30 minutes to 1.5 hours per quadrant, individual factors can extend this timeframe. Being informed about the process, preparing adequately, and following post-procedure guidelines are key to achieving optimal results. This knowledge empowers patients to approach the surgery with confidence and clarity.
Can You Chew Gum with Braces? Orthodontic Tips and Advice
You may want to see also

Factors affecting procedure time
The duration of a gum graft procedure can vary significantly, influenced by several key factors that dentists and patients alike should consider. One of the primary determinants is the extent of gum recession. Minor cases, where only one or two teeth are affected, typically take between 30 to 60 minutes. In contrast, more severe recession involving multiple teeth or larger areas can extend the procedure to 90 minutes or longer. The complexity of the case directly correlates with the time required for precise tissue placement and suturing.
Another critical factor is the type of grafting technique employed. For instance, a connective tissue graft, which involves harvesting tissue from the palate, is more time-consuming due to the additional step of tissue extraction. This method often takes 60 to 90 minutes. On the other hand, a free gingival graft, which also uses palatal tissue but in a simpler manner, may take slightly less time. Alternatively, pedicle grafts, which use adjacent gum tissue, can be quicker but are limited to specific cases. The choice of technique depends on the patient’s anatomy and the dentist’s expertise, both of which impact procedure time.
The patient’s overall health and anatomy also play a significant role. For example, patients with dense bone structure or extensive scarring from previous procedures may require more time for tissue manipulation. Additionally, individuals with conditions like diabetes or those taking medications that affect blood clotting may experience prolonged procedure times due to the need for extra precautions. Dentists often assess these factors during pre-operative consultations to estimate the duration accurately.
Finally, the dentist’s experience and skill level cannot be overlooked. A seasoned periodontist with extensive experience in gum grafting can often complete the procedure more efficiently than a less experienced practitioner. However, this does not compromise the quality of care; rather, it reflects the dentist’s ability to navigate complexities swiftly. Patients should inquire about their dentist’s expertise to set realistic expectations regarding procedure time and outcomes. Understanding these factors empowers patients to prepare adequately and ensures a smoother experience.
Dentures In or Out: Which Speeds Up Gum Healing?
You may want to see also

Post-procedure recovery timeline
The first 24–48 hours after a gum graft procedure are critical for minimizing discomfort and promoting healing. During this period, swelling and mild to moderate pain are common, but they can be managed with prescribed pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Avoid aspirin, as it can increase bleeding. Apply ice packs to the affected area in 15-minute intervals to reduce swelling. It’s essential to rest and avoid strenuous activities, as increased blood flow can disrupt the graft site. Stick to a soft, cool diet—think yogurt, mashed potatoes, and smoothies—and avoid hot, spicy, or crunchy foods that could irritate the surgical area. Most importantly, do not rinse your mouth or spit forcefully, as this can dislodge the graft.
By days 3–7, initial discomfort should subside, but the healing process is still delicate. You may notice some bleeding or oozing, which is normal unless it persists or becomes heavy. Continue with a soft diet and gradually introduce slightly firmer foods as tolerated. Oral hygiene is crucial but must be modified: gently brush teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush, avoiding the graft site, and use a prescribed antimicrobial mouthwash to prevent infection. Avoid using dental floss or water flossers near the graft until your dentist gives the green light, typically around 2 weeks post-procedure. This phase is about balance—maintaining cleanliness without disturbing the healing tissue.
Weeks 2–4 mark the transition to more robust healing, though complete recovery can take up to 3 months. By this stage, most patients can resume normal brushing and flossing routines, though care should still be taken around the graft site. Swelling and sensitivity should significantly decrease, but some discomfort may persist, especially when consuming hot or cold foods. Follow-up appointments with your dentist are essential to monitor healing and address any concerns. If you experience persistent pain, excessive bleeding, or signs of infection (e.g., pus, fever), contact your dentist immediately.
Long-term recovery focuses on maintaining gum health to ensure the graft’s success. Avoid tobacco products, as they impair healing and increase the risk of graft failure. Practice consistent oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. Be mindful of habits like teeth grinding, which can damage the graft, and consider a night guard if necessary. While the procedure itself may take only 1–2 hours, the recovery timeline spans weeks to months, requiring patience and adherence to post-operative care guidelines. By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth recovery and enjoy the long-term benefits of a healthier gumline.
Gum Graft Healing Time: What to Expect After Surgery
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A gum graft procedure usually takes between 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity and the number of areas being treated.
Yes, the type of gum graft can impact the time. For example, a connective tissue graft may take longer than a free gingival graft or a pedicle graft.
While the procedure itself is relatively quick, recovery can take 1 to 2 weeks, during which patients need to follow post-operative care instructions to ensure proper healing.