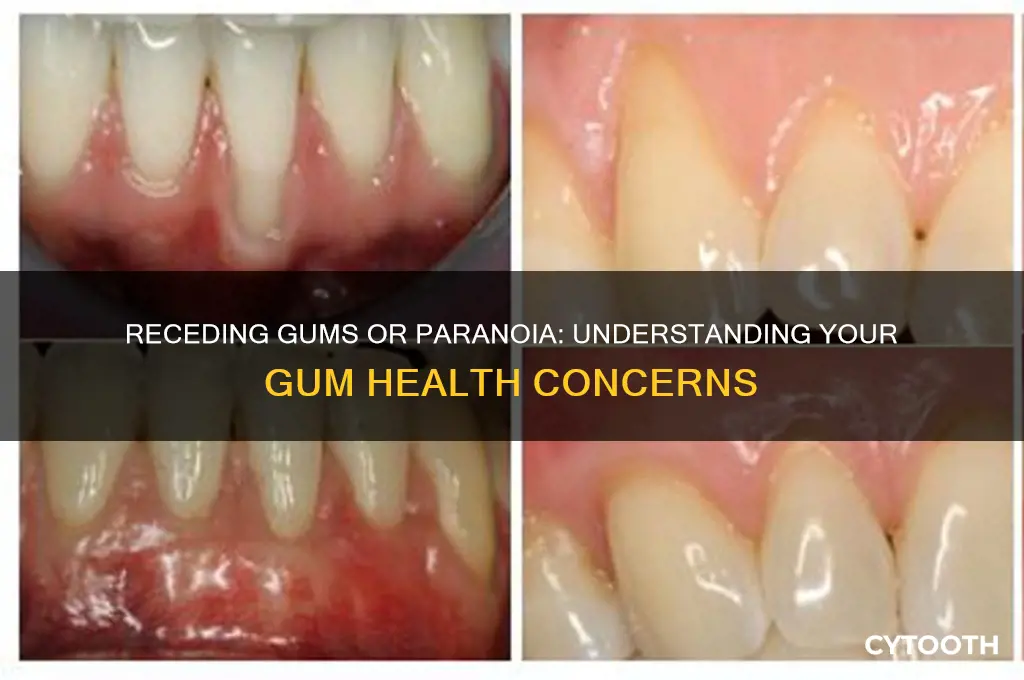
If you've noticed changes in your gum line and are wondering, Are my gums receding, or am I just paranoid? you're not alone. Gum recession is a common dental concern that can occur gradually, often going unnoticed until it becomes more pronounced. Symptoms may include tooth sensitivity, visible tooth roots, or a longer appearance of your teeth. While it’s easy to second-guess yourself, these signs shouldn’t be ignored, as gum recession can lead to more serious oral health issues if left untreated. Factors like aggressive brushing, gum disease, aging, or genetic predisposition can contribute to this condition. Consulting a dentist is the best way to determine whether your concerns are valid or simply a result of heightened awareness, ensuring you receive proper guidance and care.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Gum Recession | Visible exposure of tooth roots, teeth appearing longer, gaps between teeth and gums, sensitivity to hot/cold, and potential tooth mobility. |
| Common Causes | Poor oral hygiene, aggressive brushing, periodontal disease, genetic factors, hormonal changes, tobacco use, and misaligned teeth. |
| Symptoms | Tooth sensitivity, visible notches or gaps at the gum line, bleeding gums, bad breath, and changes in bite alignment. |
| Diagnosis | Dental examination, X-rays, and measurement of gum pocket depths. |
| Treatment Options | Improved oral hygiene, deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), gum graft surgery, and orthodontic treatment. |
| Prevention | Gentle brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush, regular flossing, routine dental check-ups, and avoiding tobacco products. |
| When to See a Dentist | If you notice persistent symptoms like sensitivity, bleeding gums, or visible changes in gum appearance. |
| Paranoia vs. Reality | Paranoia may stem from minor changes or normal anatomical variations; a dentist can provide a definitive assessment. |
What You'll Learn

Common Signs of Gum Recession
Gum recession is a gradual process, often so subtle that you might question whether it's happening at all. One of the earliest and most noticeable signs is tooth sensitivity. If you wince while sipping hot coffee or biting into ice cream, it could be more than just a fleeting sensation. This sensitivity occurs because the protective gum tissue has pulled away, exposing the tooth's root, which lacks the protective enamel of the crown. Over time, this exposure can lead to discomfort that’s hard to ignore.
Another telltale sign is the appearance of your teeth. Receding gums can make teeth seem longer than they actually are, creating an uneven or "toothy" smile. If you notice that your teeth appear larger at the gum line or that spaces between teeth seem more pronounced, it’s worth examining closer. A simple at-home test involves using a dental mirror to inspect your gum line for irregularities or areas where the tooth root is visible.
Bleeding gums, often dismissed as a minor issue, can also signal gum recession, especially if it occurs during brushing or flossing. Healthy gums should not bleed easily. If you’re experiencing persistent bleeding, it may indicate inflammation or the early stages of gum disease, both of which contribute to recession. Pair this with a receding gum line, and it’s a clear red flag that warrants attention.
Finally, changes in gum color or texture can provide critical clues. Healthy gums are firm and coral pink, but receding gums may appear red, swollen, or tender. In advanced cases, the gum tissue might thin out, becoming more translucent or developing a notched appearance. If you notice these changes, it’s not paranoia—it’s your body signaling that something is amiss. Early intervention, such as improving oral hygiene or seeking professional care, can prevent further damage and preserve your smile.

Causes of Gum Recession
Gum recession is a gradual process, often subtle enough to make you question whether it's happening at all. But several factors can contribute to this oral health concern, and understanding them is the first step in addressing it. One of the primary culprits is poor oral hygiene. When plaque and tartar build up along the gum line, they can irritate and inflame the gums, leading to a condition called gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis progresses to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that destroys the tissues and bone supporting your teeth, causing gums to recede. Brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing daily are essential, but overzealous brushing can also be harmful. Applying too much pressure or using a hard-bristled brush can wear away enamel and damage gums, accelerating recession.
Another significant cause of gum recession is genetics. Just as you inherit traits like eye color or hair texture, your genetic makeup can predispose you to thinner, more fragile gum tissue. Studies suggest that up to 30% of the population may be genetically susceptible to gum disease, regardless of oral hygiene habits. If your parents or siblings have experienced gum recession, you’re at a higher risk. While you can’t change your genetics, knowing your family history allows you to take proactive measures, such as regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings every six months.
Hormonal changes also play a role in gum health, particularly in women. Fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to recession. For instance, increased progesterone and estrogen levels during pregnancy can heighten the inflammatory response to plaque, leading to a condition known as pregnancy gingivitis. Similarly, menopause can cause dry mouth and reduced saliva production, which diminishes the mouth’s natural defense against bacteria. Using alcohol-free mouthwash and staying hydrated can help mitigate these effects.
Habits like smoking and teeth grinding (bruxism) are additional contributors to gum recession. Smoking impairs blood flow to the gums, hindering nutrient delivery and waste removal, which slows healing and exacerbates gum disease. Bruxism, often unconscious and stress-related, places excessive force on the teeth and gums, leading to tissue damage over time. If you grind your teeth, especially at night, consider using a custom-fitted mouthguard to protect your gums and teeth. Quitting smoking, meanwhile, not only benefits your gums but also reduces the risk of other serious health issues.
Lastly, misaligned teeth or improper dental work can create uneven pressure on the gums, leading to recession. Crowded teeth or bite issues make it harder to clean effectively, allowing plaque to accumulate in hard-to-reach areas. Similarly, poorly fitted dental appliances, such as braces or dentures, can irritate gum tissue. Orthodontic treatment to correct alignment issues or adjustments to dental work by a professional can alleviate these problems. Regular monitoring by a dentist ensures that any potential issues are caught early, preventing further recession.

How to Measure Gum Health
Gum recession is a gradual process, often so subtle that you might question whether it's happening at all. But ignoring early signs can lead to irreversible damage. Measuring gum health isn't just about aesthetics; it's about preserving the foundation of your teeth. One effective method is the probing depth measurement, performed by a dentist using a periodontal probe. Healthy gums typically measure 1-3 millimeters in depth. Anything beyond 3 millimeters could indicate the onset of gum disease. This simple, painless procedure provides a baseline for tracking changes over time, helping you and your dentist catch issues before they escalate.
If you’re monitoring gum health at home, look for visible cues like tooth sensitivity, longer-appearing teeth, or exposed roots. A practical tip is to gently pull back your gum tissue with a clean finger (after washing your hands) and observe the color and texture. Healthy gums are firm, pale pink, and snug against the teeth. Redness, swelling, or a spongy texture could signal inflammation. Pair this with a daily habit of checking for bleeding while brushing or flossing—healthy gums shouldn’t bleed easily. These self-assessments, while not definitive, can prompt timely professional evaluation.
For a more structured approach, consider the Gum Bleeding Index, a tool used in dental studies but adaptable for personal use. Score each tooth on a scale of 0 to 3 based on bleeding after flossing: 0 for no bleed, 1 for slight bleeding, 2 for immediate bleeding, and 3 for spontaneous bleeding. A cumulative score above 5 suggests potential gum issues. This method quantifies your observations, making it easier to track changes over weeks or months. Combine it with regular dental check-ups for a comprehensive view of your gum health.
Lastly, technology offers tools like smart toothbrushes with pressure sensors and apps that track brushing habits, indirectly supporting gum health by preventing over-brushing. While not a direct measurement, these devices can highlight behaviors contributing to gum recession. Pairing tech with traditional methods creates a holistic approach to monitoring gum health, ensuring you’re neither paranoid nor neglectful. Remember, early detection is key—whether through a probe, visual cues, or digital tools, staying proactive protects your smile’s foundation.

When to See a Dentist
Gum recession is a gradual process, often so subtle that you might question whether it's happening at all. But here’s the reality: if you’re noticing your teeth appear longer, experiencing increased sensitivity to hot or cold, or spotting pink along the gumline when you brush, it’s time to stop second-guessing and take action. These signs aren’t just in your head—they’re red flags your mouth is waving at you.
While minor gum changes can sometimes be managed at home with diligent oral care, certain symptoms demand professional attention. If you’re bleeding every time you brush or floss, have persistent bad breath despite regular hygiene, or notice a notch or indentation where your gums meet your teeth, don’t wait. These are not normal, and ignoring them could lead to irreversible damage like tooth loss or bone deterioration.
Here’s a rule of thumb: if you’re asking yourself, “Are my gums receding?” the answer is likely yes, at least to some degree. The question now is *how much* and *why*. A dentist can measure recession depth, identify underlying causes (like aggressive brushing, misalignment, or gum disease), and recommend targeted treatments. Scaling and root planing, gum grafts, or even orthodontic adjustments might be necessary—solutions only a professional can provide.
Don’t let fear or uncertainty delay your visit. Gum recession doesn’t reverse on its own, and early intervention is key to preserving your oral health. Think of it this way: seeing a dentist isn’t just about fixing a problem—it’s about preventing one from escalating. Your gums are a window to your overall health, and ignoring their cries for help could have far-reaching consequences.

Preventing Gum Recession
Gum recession is a gradual process, often so subtle that you might question whether it's happening at all. But ignoring early signs can lead to irreversible damage. The good news? Prevention is within your control. Let's explore actionable strategies to safeguard your gumline.
Brush Like a Pro, Not a Bulldozer
Aggressive brushing is a leading culprit behind receding gums. Stiff-bristled toothbrushes and forceful scrubbing erode enamel and irritate gums. Switch to a soft-bristled brush and adopt the Bass technique: tilt the brush at a 45-degree angle to the gumline, using gentle circular motions. Electric toothbrushes with pressure sensors can also prevent overzealous cleaning. Aim for 2 minutes twice daily—no more, no less.
Floss Daily, But Strategically
Skipping flossing accelerates plaque buildup, which hardens into tartar, a major driver of gum recession. However, snapping floss violently between teeth can traumatize gums. Instead, curve it around each tooth in a "C" shape and glide it gently up and down. For tight spaces, try waxed floss or a water flosser. Consistency matters: make it a nightly habit, not a sporadic effort.
Mind Your Bite: Bruxism and Beyond
Teeth grinding (bruxism) exerts excessive force on gums and teeth, accelerating recession. If you wake with jaw soreness or headaches, you’re likely a grinder. A custom night guard, fitted by your dentist, can redistribute pressure. Stress reduction techniques—yoga, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation—may also curb grinding. Avoid chewing hard objects (ice, pens) to minimize additional strain.
Nutrition: The Unsung Hero
Deficiencies in vitamin C, vitamin D, and calcium weaken gums and bones, making recession more likely. Incorporate citrus fruits, leafy greens, dairy, and fortified foods into your diet. For targeted support, consider supplements: 1,000 mg of vitamin C and 1,000–2,000 IU of vitamin D3 daily (consult a doctor first). Stay hydrated—dry mouth reduces saliva, which naturally protects gums from bacteria.
Regular Check-Ups: Your Early Warning System
Gum recession often progresses silently until it’s advanced. Biannual dental visits allow professionals to spot early signs—like deepening pockets or exposed roots—and intervene. Hygienists can remove tartar buildup you can’t tackle at home. If recession is detected, treatments like deep cleaning or gum grafting may be recommended to halt progression.
By combining these strategies, you shift from passive observer to active protector of your oral health. Prevention isn’t just possible—it’s practical. Start today, before questioning turns into regret.
Frequently asked questions
Look for signs like tooth sensitivity, visible gaps between teeth and gums, or teeth appearing longer than before. If you notice these changes, consult a dentist for a proper evaluation.
Mild gum recession can occur with age, but significant or sudden recession may indicate gum disease, aggressive brushing, or other issues. A dentist can determine if it’s normal or problematic.
Stress and anxiety can heighten awareness of oral sensations, but they don’t cause physical gum recession. If you’re unsure, a dental checkup can provide clarity.
Trust your dentist’s professional assessment, but monitor your oral health and maintain good hygiene. If concerns persist, seek a second opinion for peace of mind.

